
Successful healing of all wounds whether traumatic or surgical involves a good understanding of wound healing and biosecurity principles.
"A wound is a break or opening in the skin."
This break in the skin is a break in the body’s natural defensive barrier and makes patients susceptible to infection. The susceptibility of a patient to succumbing to a wound infection depends upon several factors. At Pioneer we offer support to practices to look at implementing pro-active protocols to reduce the likelihood of surgical wound breakdowns.
Wound Dehiscence
Wound Dehiscence is when the edges of a wound, which have previously been approximated (usually sutured closed), open and/or rupture, therefore failing to heal. This is normally noted at around 5 to 8 days post closure. Therefore, the aftercare of the wound at home with the patient's owner is equally important. It is the practice’s responsibility to educate the owner on how to correctly look after the wound and the signs of wound complications, so that intervention can be instigated as soon as practicable.
We have been presented with several non-healing surgical wounds, from infected to complete breakdown. Here are a few images of those that we have assisted with.
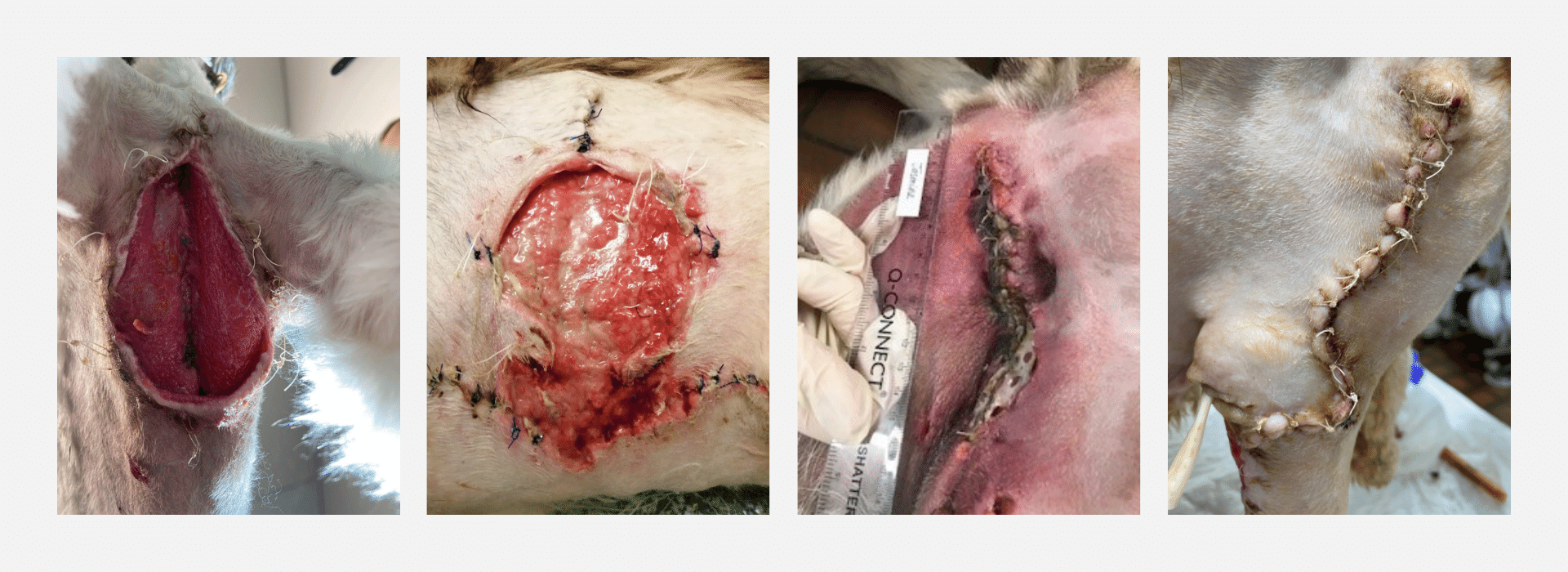
In practice, it's essential to implement gold standards and set out everyday practices that help reduce the likelihood of any surgical wound breakdowns, thus ensuring wounds healing by primary intention are timely, pain and complication free.
Considerations For Preventing Surgical Wound Breakdowns
Below is a list of considerations and easy-to-implement actions for preventing surgical wound breakdown.
Clippers
Clipper blades can harbour bacteria very quickly, so these must be changed/disinfected appropriately/ after each patient and at the end of the day. In addition to removing hair, spraying them with a broad spectrum disinfectant spray in-between patients is recommended. Clinell Universal Disinfectant Spray has a quick activation time and is handy for everyday use. Clipper blades can also be soaked in disinfectant solution at the end of each day – on their own, not in with your instruments, and then dried, oiled and lubricated, ready for the next day. There should be a separate pair of clippers for each area of the building and a separate pair for clipping wounds.
We have a handy free clipper cleaning guide to assist practices in carrying out the correct regime available - this is available in your resources section of your web account.
Theatre Hoover
Hoover filters need to be changed or disinfected daily – filters should be changed regularly as, again they can harbour and redistribute bacteria quickly.
Correct Dilution Rates of Skin Scrub
It is recommended a 50:50 rate of Chlorhexidine 4% is used for surgical wound preparation. Prepare a fresh bowl of solution with warm water for each patient.
Environmental Cleaning
Is everyone in practice using the recommended dilution rates for cleaning surfaces and floors? Surfaces should be cleaned regularly with appropriate disinfectants between patients and the area left to dry so the correct contact times are effective. Ensure you check the manufacturer's contact times and dilution rates for each surface disinfectant used.
There should also be suitable protocols in place for regular cleaning of kennels and cattery. Effective environmental decontamination is paramount in reducing the chances of any bacteria in the area reaching the patient's wounds.
Wound Closure
As a rule, surgical wounds are considered clean, however, in the instance of contamination or evidence of devitalised tissue, the wound should be left open for approximately 3 to 4 days. This delayed primary closure allows time to determine if there is infection present or if the tissues continue to devitalise.
Post-Operative Dressings
All surgical wounds need to be covered for at least 48hrs. It is considered best practice to cover all surgical incisions post-procedure - when practical, this should involve low adherence, and transparent polyurethane dressings. These protect the wound and allow you to check the surgical incision site for any signs of wound infection without disturbing the dressing or healing the surgical site itself. These dressings can be left in place for between 3 and 5 days, during which the epithelialisation process may be completed in a wound healing by primary intention.
We recommend that a dressings protocol be put into place, and the price factored into your procedure cost to clients. A post-op dressing information sheet should help clients understand the importance of dressing surgical wounds.
Swabbing
Staff and surfaces should be swabbed ideally every 6 months. Particularly for MRSA, especially if you are involved in high amounts of procedures, such as orthopaedics. If swabbing surfaces, as well as swabbing "Touch Points", it is beneficial also to be swabbing places such as under tables or whiteboard markers, areas where people often forget to clean. This is then a good indication of how well your practice decontaminates. The Clinell Evaluclean UV Torch Kit can assist with auditing your cleaning protocols.
Infection Control Protocols
We offer support to assist practices with creating gold standard infection control protocols. Fill in the form below, detailing what you require assistance with, and we'll be in touch.








